Force on a Moving Charge
Force on a Moving Charge: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Magnetic Force, Force on a Moving Charge in Magnetic Field, Radius of Curvature of the Helical Path in Magnetic Field & Position of the Charged Particle in Helical Path in Magnetic Field etc.
Important Questions on Force on a Moving Charge
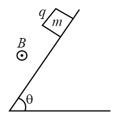
A block of mass and charge is released on a long smooth inclined plane. Magnetic field is constant, uniform and out of the plane of the paper as shown. Find the time from the start when block leaves contact with the surface.
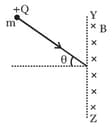
A particle with charge +Q and mass m enters a magnetic field of magnitude B, existing only to the right of the boundary YZ. The direction of the motion of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of B.
. The time spent by the particle in the field will be
Two particles of charges +Q and -Q are projected from the same point with a velocity v in a region of uniform magnetic field B such that the velocity vector makes an angle θ with the magnetic field. Their masses are M and 2M, respectively. Then, they will meet again for the first time at a point whose distance from the point of projection is
An electron moving with a velocity at a point in a magnetic field experiences a force . If the electron is moving with a velocity at the same point, it experiences a force . The force the electron would experience if it were moving with a velocity at the same point is
A particle of specific charge (charge/mass) α starts moving from the origin under the action of an electric field and magnetic field . Its velocity at is . The value of is :
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of uniform electric and magnetic fields, which are parallel to each other. The locus of the particle will be
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of uniform electric and magnetic fields, which are parallel to each other. The locus of the particle will be
A particle having charge of , mass and speed enters a uniform magnetic field, having magnetic induction of , at an angle between velocity vector and magnetic induction. The pitch of its helical path is (in meters)
Electrons moving with different speeds enter a uniform magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the field. They will move along circular paths,
An electron experiences no deflection, if subjected to an electric field of and a magnetic field of . Both the fields are normal to the path of an electron and to each other. If the electric field is removed, then the electron will revolve in an orbit of radius
An electron having kinetic energy T is moving in a circular orbit of radius R perpendicular to a uniform magnetic induction . If kinetic energy is doubled and magnetic induction tripled, the radius will become
A uniform magnetic field exists in a space. A particle of mass and charge q is projected towards negative x- axis with speed v from the a point (d, 0, 0). The maximum value v for which the particle does not hit y-z plane is
An electron is projected with velocity in a uniform electric field E perpendicular to the field. Again it is projected with velocity perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B/If is initial radius of curvature just after entering in the electric field and is initial radius of curvature just after entering in magnetic field then the ratio is equal to
A particle of charge and mass starts moving from the origin under the action of an electric field with velocity The speed of the particle will become after a time
An electron is moving along a positive axis. A uniform electric field exists towards negative axis. What should be the direction of a magnetic field of suitable magnitude, so that the net force of electron is zero.
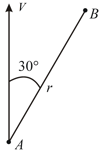
A charge particle of charge has velocity . When it passes through point and has velocity in the direction shown. The strength of magnetic field at point due to this moving charge is .
Two long parallel wires are at a distance 2d apart. They carry steady equal currents flowing out of the plane of the paper, as shown. The variation of the magnetic field B along the XX' is given by
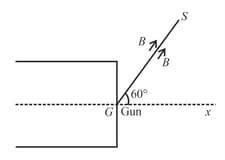
An electron gun G emits electron of energy travelling in the (+)ve x-direction. The electrons are required to hit the spot S where & the line GS makes an angle of with the x-axis, as shown in the fig. A uniform magnetic field parallel to GS exists in the region outsides to electron gun. Find the minimum value of B needed to make the electron hit S.
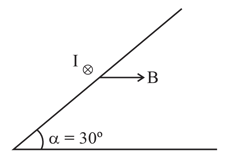
The figure shows a conductor of weight 1.0 N and length L = 0.5 m placed on a rough inclined plane making an angle with horizontal so that conductor is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of induction B = 0.1T. The coefficient of static friction between the conductor and the plane is 0.1, A current of I = 10A flows through the conductor inside the plane of this
paper as shown.
What is the force needed to be applied parallel to the inclined plane to sustain the conductor at rest.
A particle of charge+q and mass m moving under the influence of a uniform electric field E enters in I quadrant of a coordinate system at a point (0, a) with initial velocity vand leaves the quadrant at a point (2a, 0) with velocity .
Find Magnitude of electric field
